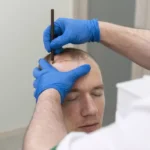
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive procedure, and it is used to treat certain mental health conditions. It uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, without requiring surgery or anesthesia. This option is available to you if medication has not provided sufficient relief for your symptoms. While the science sounds complex, the mechanism relies on principles of magnetic induction and brain connectivity.
Magnetic Pulses in TMS
The core component of TMS therapy is an electromagnetic coil placed against your scalp. This coil generates short magnetic pulses, which pass easily through the skull into the brain. The magnetic field induces small electrical currents that stimulate nerve cells in the targeted region. This stimulation activates underactive neurons or calms overactive ones, based on your provider’s protocol. When neurons fire more consistently, brain chemistry changes, and communication between brain regions becomes more efficient. This process is called neuromodulation. It trains brain circuits, so they function more effectively without the need for medication.
Specific Conditions
Different mental health conditions involve different areas of the brain that require specific attention. For depression, the treatment targets the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. This area is often underactive in people with major depressive disorder. The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex helps regulate emotions, planning, and complex thinking, and when underactive, it leads to low mood and a lack of motivation. TMS activates this region and strengthens neural pathways involved in mood regulation and emotional control. For anxiety, treatment sometimes expands to include regions such as the right prefrontal cortex. This is linked to worry and heightened alertness. By influencing these areas, TMS encourages greater balance between the brain systems. Anxiety often co-exists with depression, so some protocols address symptoms of anxiety during the same treatment course.
OCD and Smoking Cessation
TMS is also FDA-cleared for treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), and it helps with smoking cessation. In OCD treatment, the magnetic coil targets a different brain region involved in the control of repetitive thoughts and behaviors. TMS disrupts the repetitive signals that create compulsive actions. Repeated sessions help the brain develop new, healthier response patterns. The stimulation regulates hyperactivity in these circuits. Patients manage their compulsions and intrusive thoughts without intense distress.
For smoking cessation, the treatment focuses on the insula and the prefrontal cortex. These areas are involved in addiction, and they send craving signals. TMS lowers the response of neural pathways linked to addiction triggers. This reduces cravings and supports efforts to quit. The magnetic pulses make it easier to resist the urge to smoke cigarettes. By disrupting neural patterns linked to addiction, TMS helps break the cycle of dependence.
Take the Next Step
TMS therapy offers a scientifically grounded alternative for several mental health conditions. The treatment is conducted in an office setting. You return to your daily activities immediately after each session, and it addresses the biological roots of symptoms. Because the treatment avoids some side effects, it can be preferred over traditional medications. If you struggle with depression, OCD, or smoking addiction, consult a healthcare provider about your eligibility. A healthcare provider reviews your medical history and determines whether this non-invasive technology aligns with your recovery goals.