The human foot contains bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments; this intricate structure supports the body’s weight and provides leverage for movement. Persistent foot pain can indicate an underlying condition that requires attention. Understanding the sources of foot discomfort helps individuals determine when to seek professional care, such as orthotics or diabetic wound care.
What Causes Foot Pain?
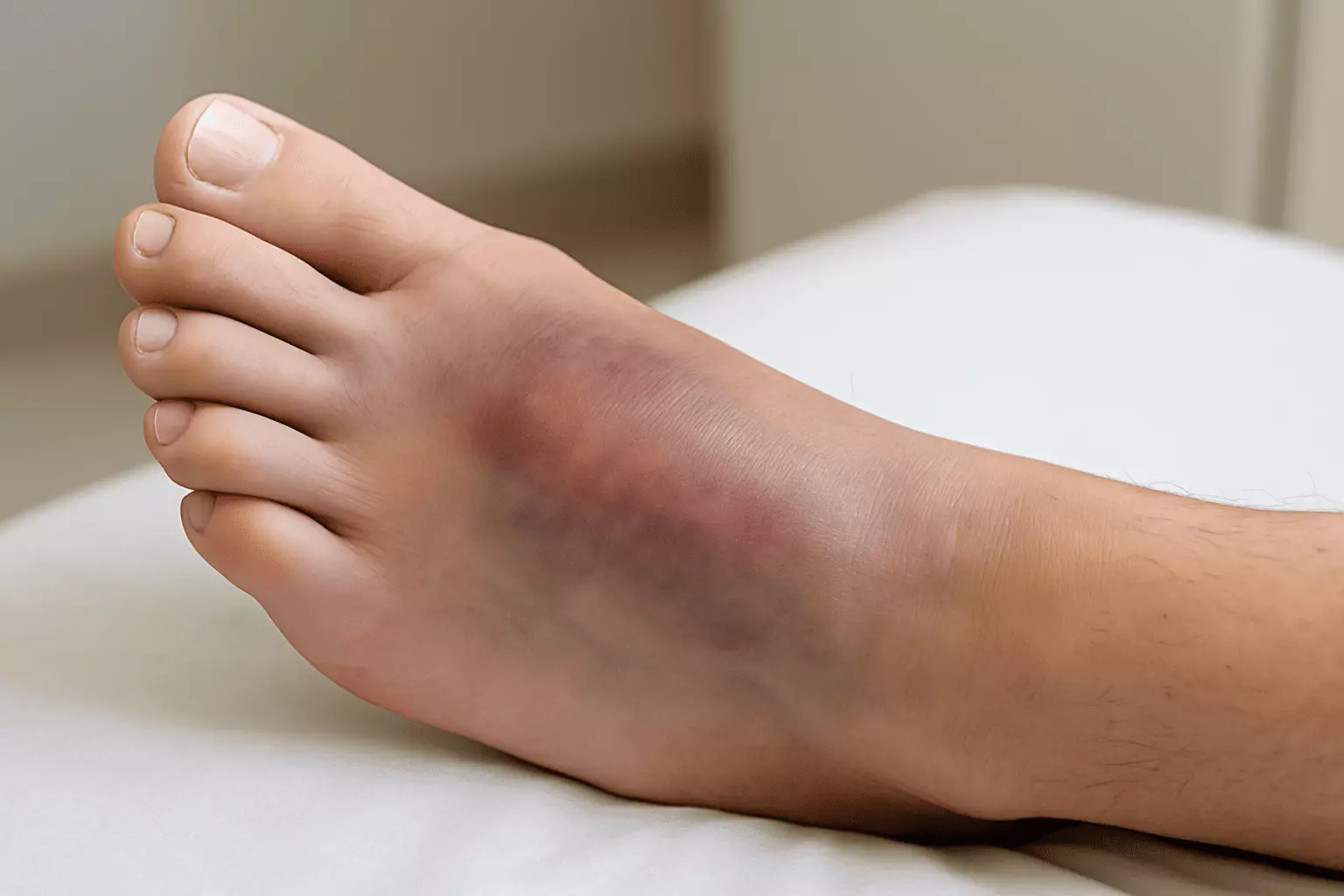
Foot pain can originate from various sources, including biomechanical issues, injuries, and systemic health conditions. Inherited foot structures may predispose individuals to pain. Flat feet or high arches alter the distribution of weight, placing excessive stress on certain muscles and joints. Other common structural problems include bunions and hammertoes, where bones shift out of proper alignment and cause friction and inflammation.
Overuse Injuries
Repetitive activity is a frequent cause of foot injuries. Plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue band connecting the heel to the toes, is a common condition resulting in sharp heel pain. Achilles tendinitis is inflammation of the tendon linking the calf muscles to the heel, which often affects athletes who rapidly increase their training intensity.
Systemic Conditions
Certain medical conditions can manifest as foot pain. Arthritis, including both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, leads to joint inflammation and stiffness. Diabetes may cause peripheral neuropathy, which results in numbness or tingling sensations that may mask injuries.
How Can Pain Be Prevented?
Preventative measures focus on reducing stress on the feet and maintaining overall foot health. Simple lifestyle adjustments can provide substantial benefits. Select shoes designed for the specific activity, as walking and running shoes may offer different types of support and cushioning. Excess body weight increases the mechanical load on the feet. Reducing weight can lessen the stress on bones, joints, and ligaments, lowering the risk of developing or worsening foot pain.
How Is It Treated?
Treatment approaches vary based on the specific diagnosis. Many conditions respond well to conservative management. For acute injuries, the R.I.C.E. protocol is effective for managing inflammation and swelling; it stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Applying ice multiple times a day can reduce pain.
Orthotics and Medication
Custom or over-the-counter shoe inserts may correct biomechanical imbalances. Arch supports help distribute weight evenly, while heel inserts can provide cushioning for conditions like plantar fasciitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce pain and inflammation, and corticosteroid injections may be used for targeted relief of severe inflammation.
Diabetic Wound Care
Individuals with diabetes require specialized foot care. Diabetes may impair sensation and circulation, delaying wound healing and increasing infection risk. Daily foot inspection is recommended to identify sores or cuts early. Keeping wounds clean and using appropriate dressings via diabetic wound care practices are foundational to healing. Offloading pressure with specialized footwear helps protect vulnerable areas.
Surgical Intervention
When conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgery may be an option. Procedures can range from correcting bunions to fusing joints for severe arthritis. The goal of surgery is to restore function and alleviate chronic pain.
Confer With a Podiatrist
Persistent foot pain can limit daily activities and mobility, and a podiatrist has the specialized training to diagnose complex foot and ankle conditions. They use diagnostic tools like imaging tests and gait analysis to identify the source of discomfort. Early professional intervention may prevent minor issues from becoming chronic problems, helping to protect long-term mobility.