Recovery after surgery involves cellular repair, inflammation management, and tissue restoration. Among available supportive therapies, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is studied for its ability to aid healing. Hyperbaric therapy can be utilized as a treatment method under the supervision of healthcare professionals and may be used to enhance the recovery of a surgical incision.
What Is Hyperbaric Therapy?
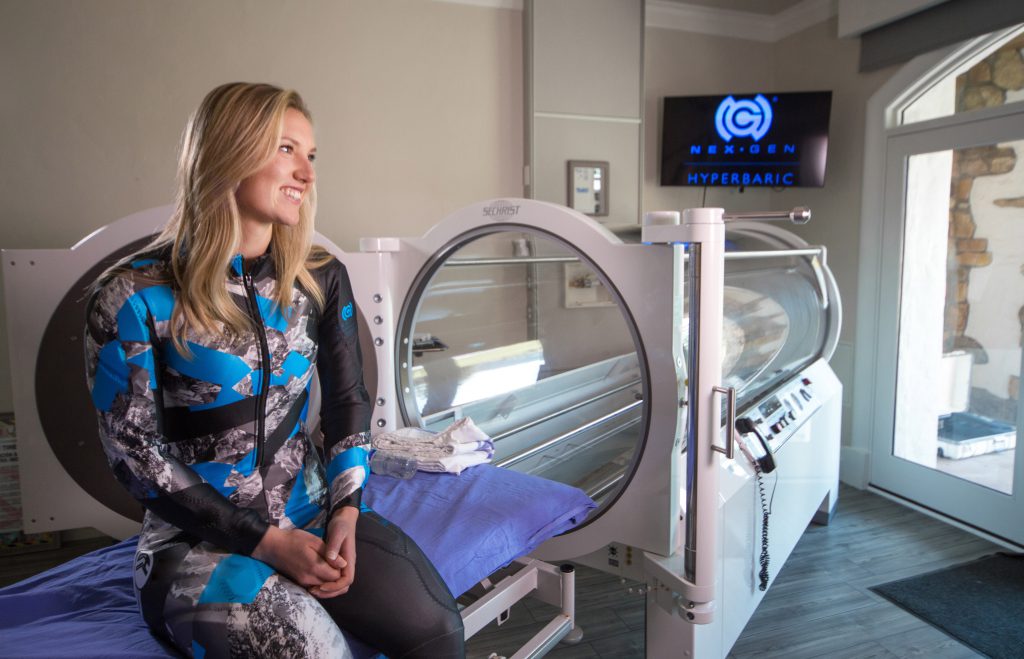
Hyperbaric therapy involves breathing pure oxygen at pressures higher than normal atmospheric levels inside a sealed chamber. This chamber may be configured for individual or multiple patients. Monoplace chambers accommodate one person in a transparent cylinder, while multiplace chambers have space for several people.
Standard air contains about 21% oxygen, but HBOT uses 100% medical-grade oxygen. A single session may vary in length based on the specific medical need and the clinical protocol determined by a medical team. The number of sessions prescribed is matched to each patient’s requirements, including their surgical history and overall health.
How Does It Work?
Oxygen movement through the body is necessary for cell function. HBOT uses pressure to cause oxygen-rich blood to reach more areas, including tissues that are recovering from surgical procedures. This surplus of oxygen supports biological processes related to healing. High levels of dissolved oxygen also assist white blood cells in defending against infection. The improved oxygen environment can address tissues that lack sufficient oxygen, which can slow healing.
What Are the Benefits?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used in a hospital setting for several medical conditions, including complex wound management and tissue injuries that are difficult to heal. Surgical healing often triggers tissue swelling as part of the recovery response. The high-pressure environment of HBOT can lead to temporary narrowing of blood vessels. This process may reduce the amount of fluid leaking into tissues, supporting decreased swelling after procedures.
Another effect observed is the growth of new blood vessels. Operations can impair small blood vessels and disrupt local circulation. HBOT stimulates the healing processes that contribute to capillary development, supporting improved blood flow where tissue demands are high during recovery.
Oxygen may be used for the synthesis of energy production within cells responsible for wound closure. Hyperbaric conditions amplify these natural mechanisms, supporting the healing of surgical incisions, grafts, and flaps. The presence of high-level oxygen also enhances the body’s ability to fight certain bacteria, which can be relevant for post-operative infection risk. Within clinical settings, hyperbaric therapy follows protocols set by specialized physicians. Conditions such as compromised skin grafts, chronic wounds, and certain infections have been treated with HBOT. Recovery protocols can be adapted for each of these use cases.
Seek Care From a Specialist
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a medical treatment that is carefully supervised and tailored to an individual’s needs. Patients interested in this therapy for post-surgical recovery can consult with a healthcare provider trained in hyperbaric medicine, discussing potential risks and benefits. Such a specialist will evaluate the surgical history and overall medical condition, and provide information on treatment protocols, session expectations, and suitability for HBOT as part of a recovery plan.